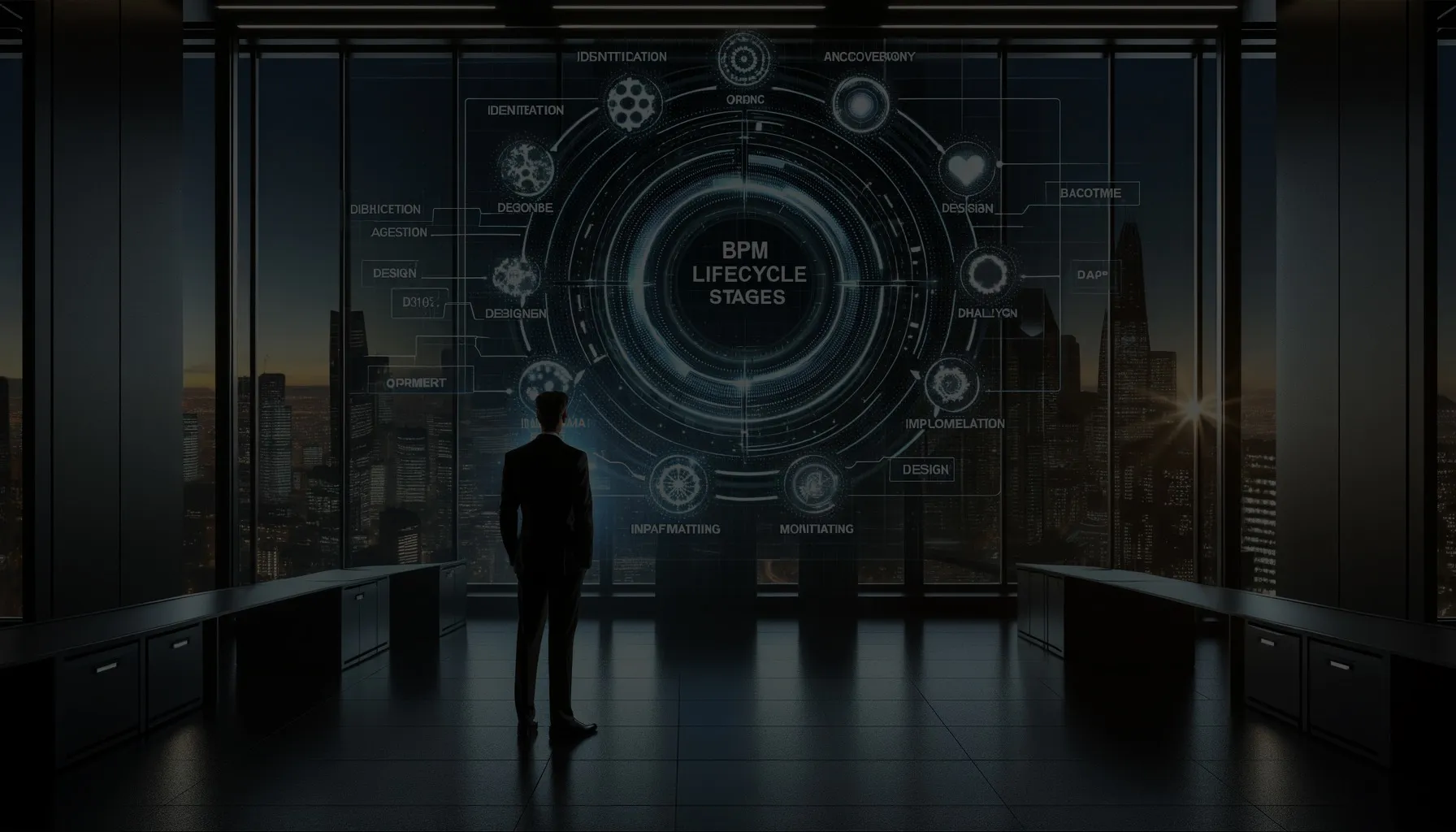
In the contemporary economic landscape, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) play a pivotal role in driving innovation, job creation, and overall growth. With Forbes reporting that 99.9% of U.S. businesses classify as SMEs, employing a significant portion of the workforce, the critical contribution of these enterprises to the economy is undeniable. To navigate the challenges of an ever-evolving marketplace, SMEs are increasingly turning to Business Process Management (BPM) as a systematic approach to enhance operational efficiency and achieve strategic goals. This comprehensive article explores the BPM lifecycle, detailing its importance, the stages involved, and how implementing BPM can significantly benefit SMEs.
The Significance of BPM for SMEs
Business Process Management (BPM) is not just a buzzword but a structured methodology that helps organizations, especially SMEs, design, execute, manage, and optimize their business processes. In an era where efficiency and agility are paramount, BPM offers a way to streamline repetitive tasks such as employee onboarding, contract approvals, leave applications, and invoice management. By adopting the BPM lifecycle, SMEs can ensure these processes are performed with greater consistency, leading directly to improved business outcomes.
Understanding the BPM Lifecycle
The BPM lifecycle comprises five phases: Design, Model, Execute, Monitor, and Optimize. This iterative approach ensures that processes are continually refined and improved, allowing businesses to adapt to changing market demands and internal goals.
- Design Phase: This foundational stage involves analyzing current processes to identify inefficiencies and areas for improvement. It sets the direction for the BPM initiative, focusing on eliminating bottlenecks and streamlining process flows.
- Model Phase: Building on the design phase, modeling involves creating detailed representations of the redesigned processes. This stage is crucial for visualizing potential improvements and involves stakeholder engagement to ensure all perspectives are considered.
- Execute Phase: The execution stage brings the redesigned processes to life. It often includes a pilot test to identify and address any issues before full-scale implementation, ensuring the new processes perform as intended.
- Monitor Phase: Once implemented, the monitor phase is essential for evaluating the performance of the new processes. Tracking key metrics and KPIs provides insights into whether the processes are meeting their intended goals and where further adjustments are needed.
- Optimize Phase: The final phase focuses on refining processes based on insights gained from monitoring. This stage embodies continuous improvement, aiming to enhance efficiency and effectiveness in business operations.
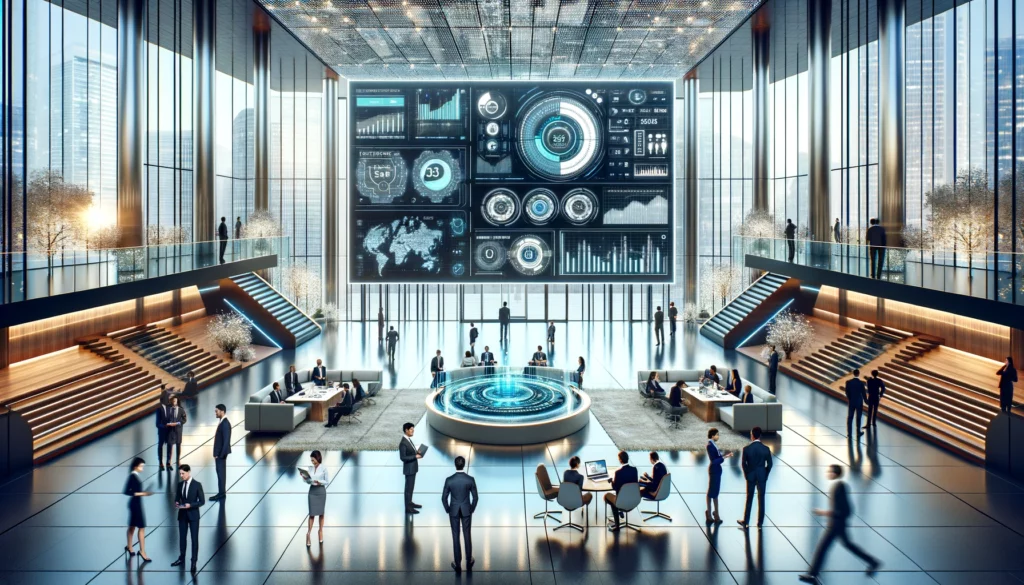

Types of BPM and Their Relevance to SMEs
Understanding the different types of BPM is crucial for tailoring the approach to an organization’s specific needs. BPM can be categorized into three main types: Human-centric, Document-centric, and Integration-centric BPM.
- Human-centric BPM revolves around processes that require significant human involvement, often in creative tasks where decision-making is key, such as customer service operations.
- Document-centric BPM focuses on managing paper-based and electronic documents within processes that need to adhere to company policies, industry standards, and regulatory requirements, typical of legal and accounting procedures.
- Integration-centric BPM, or System-centric BPM, emphasizes the automation and integration of systems like ERP, CRM, and HRMS, enhancing efficiency and user satisfaction through streamlined access to applications, data, and services.
The Role of BPM Automation Tools
For SMEs, BPM automation tools like Tasky Cloud represent a transformative opportunity to automate routine processes directly within familiar platforms. Tasky’s workflows automate common processes while tickets manage issues, demonstrating how BPM tools can significantly improve operational efficiency and communication.
Navigating the BPM Lifecycle Successfully
Implementing BPM requires a well-planned strategy that involves key stakeholders early, prioritizes processes for improvement, leverages automation, and commits to continuous monitoring and improvement.
The Cultural Impact on BPM Implementation
The success of BPM initiatives is deeply influenced by an organization’s culture. A culture that values collaboration, open communication, and adaptability can significantly enhance the effectiveness of BPM stages. Conversely, a rigid culture may hinder the successful adoption of BPM practices. Therefore, fostering a culture that supports continuous improvement and values employee involvement is essential for maximizing the benefits of BPM.
Differentiating BPM from Project Management
While both BPM and project management aim to streamline operations and achieve business goals, they serve different purposes and require distinct approaches. BPM focuses on continuous process improvement and aligning processes with strategic goals, whereas project management is concerned with managing specific, temporary projects within defined timeframes.

Best Practices for BPM Implementation
Successful BPM implementation involves involving key stakeholders from the outset, prioritizing critical processes for improvement, embracing automation to eliminate manual tasks, and continuously monitoring processes for ongoing optimization. Training and support play vital roles in ensuring teams are equipped to utilize BPM tools effectively, highlighting the importance of choosing a platform like HighGear that offers comprehensive training resources and support.
Conclusion: Empowering SMEs Through BPM
The BPM lifecycle offers SMEs a strategic framework for optimizing their operations, enhancing efficiency, and driving sustainable growth. By understanding the different types of BPM, navigating the lifecycle’s stages successfully, and leveraging automation tools, SMEs can transform their business processes. This not only positions SMEs for competitive advantage in the marketplace but also contributes to the broader economic ecosystem by fostering innovation, efficiency, and resilience. As SMEs continue to navigate the complexities of the business landscape, embracing the BPM lifecycle and its principles will be instrumental in achieving long-term success and stability.